Nostalgia for the Future: Lana Del Rey’s ‘Love’ and the Cultural Politics of Celestial Hauntology and Queer Temporality
[this essay arose out of Tumblr & IRL discussions with Scott Coubrough & Douglas Pattison; all images taken as screen-caps from the ‘Love’ video unless stated otherwise]
look at you kids with their vintage music
coming through satellites while cruising
you’re part of the past
but now you’re the future
Lana Del Rey finally dropped a new song. Critics are calling it ‘uplifting’, ‘radiofriendly’, ‘an ode to allowing yourself to feel’. They aren’t wrong: on the surface, ‘Love’ does what it says on the tin. It’s a pop song dripping with sentiment, evoking that sense of yearning, the fragile desire of a typical Lana ballad, the kind of retro-culture sadcore found most prominently on Born to Die (e.g. ’Videogames’ and ‘Summertime Sadness’). However, as with all of Lana’s material, there’s more going on beneath the surface. This isn’t just a saccharine ballad about love. In fact, this is probably the most poignant address to millennial angst I’ve experienced in pop music so far.
In the video for ‘Love’, clad in a white dress, dark hair studded with sixties-style daisies, Lana’s figure fades into view out of blackness. The mood is monochrome, but the song and its video deal in more than one mood, one temporality. As Scott Coubrough puts it, ‘it totally depicts the experience of the cultural anachrony of now’ (citation: Tumblr chat). The black-and-white vintage Hollywood vibe is lingered over with sensuous closeups of smouldering cigarettes, dust swirling on a rain-streaked window, a handsome man pulling shapes from his vintage guitar. In the first half of the video, Lana’s performance is spliced around footage of kids living in a pastel-hazed Instagram version of the sixties, skateboarding and drifting in couples around graffitied streets. While most of these teenagers carry sixties iconography—huge plastic shades, cropped haircuts, Ginsberg-glasses—there are the odd anachronisms, the kind of hoodie-clad ambience of a Blink 182 video romanticised in slow-motion. Smartphones make an appearance only as cameras. It’s not a selfie that’s taken, but an old-fashioned snapshot of a friend. Why invoke this vintage idea of relationships, of summer afternoons wasted innocently without the distracting paraphernalia of everyday technology? Who are these kids, who have time to lean seductively over trucks, to laugh arm in arm in glorious LA sunlight?
This is all a deliberate exercise in nostalgia. The warm haze of an Insta-filter showers these moments in the warm glow of preservation, the stylised memorabilia we accumulate daily with our social media feeds. There’s a sense of the future anterior to everything that happens: such visual flickers of perfection, snapped as photos, remind us that youth is always about imminence: knowing that this won’t last forever, that soon it will slip away. We are always finding ways to preserve, to prolong it. Youth. Even as we’re living, we’re thinking of ways to capture the moment.
So far so ordinary. Nostalgia for lost youth and lost love isn’t exactly a new theme in pop music, from Van Morrison’s ‘Brown Eyed Girl’ to Del Rey’s own back-catalogue, notably her offering on The Great Gatsby soundtrack, ‘Young and Beautiful’: “will you still love me when I’m no longer young and beautiful?” What’s different about ‘Love’ is its relentless insistence on the temporal deferrals within presence. “To be young and in love” she sings over and over, a collective rallying cry to her fans that urges its utopian possibility through the infinitive, rather than present tense. There’s no actual sense that these kids are all in love, but Lana explores what that love really means. She references the confusion of modern dating, mired as it is in the conventions of various apps and different types of hookup (“signals crossing can get confusing”). She repeats the word “crazy” like she’s trying to conjure it into being from the word’s invocation of chaos. But other than that, ‘Love’ doesn’t explicitly explore what it means to be in a conventional relationship; there’s none of the vivid imagery of masochism and defeat, none of the apostrophised Brutish and Beautiful Men you might find scattered around previous albums. Instead, love figures on this song as a kind of energy, the channels of desire that seem to pull us out of our current reality and into nostalgic futures.
The problem is, this desire isn’t a simple longing for a lost object, the loved one who slipped from our grasp; it’s a kind of depression, the Freudian melancholia that lacks an identifiable source, that eats away at our sleep. Beneath the sugary imagery of couples sharing walks and drives together, there’s that restless unease. The dark pulse of Born to Die-era strings. The heart of the song is a sense of self-reflective stasis. The camera pulls outwards to reveal the teenagers in the ballroom, watching Lana perform with reverent awe in their faces. Already, the singer is reflecting on the cultural presence of her music as it spreads into the future through the track’s own duration. This is a song which never seems to build to obvious climax, which rejects that teleological impulse towards the goal of release and decline, the cycles of reproduction which compel us to consume more and more as we start again each time. Instead, ‘Love’ wallows in the shallows of its strange, haunted swing, mesmerising us with cinematic production, with delicately repeated refrains that twirl like spun sugar. Onstage, Lana is bathed in white light, this ethereal beacon from the past or future, existing in the timeless space of an auditorium. It’s like the set for a Beckett play, that dark space of absence and aporetic timelessness where anything might happen. Beckett, only with sex, beauty and audience adoration. We’re encouraged by a playful, irresistible wink to fall for this surreal and breathless dream.

The kids slowly sink into Lana’s music, lolling their heads in time, blinking in meditative motion as they stare at her swaying onstage. When we see the starlight reflected back through Lana’s eyes, the kids begin seeing the same celestial beauty. A huge moon rises above them, the walls of reality shattering as the ceiling becomes a super-imposed night sky. The truck starts spinning in space, a truly lost object, like the kind of anachronistic cultural products scattered across Back to the Future, divorced from their temporal ‘home’ and washed up elsewhere, the debris of a lost present. In space, the truck’s radio says ‘No Service’. We’ve entered Beth Orton’s ‘Galaxy of Emptiness’, the starry space where we’re detached from the everyday. “Back to work or the coffee shop”; these banal facts of daily life are usually excluded from the typical Lana song, which is more likely to feature gangsters and bad boys and probably a branded soft drink or declaration of deeply personal romantic sadness. This song feels more universal, generational, though nonetheless affective. The ordinariness of work and coffee (made more poignant by the obvious fact that many millennials combine the two as baristas, again reinforcing this idea of a dull labour cycle) infiltrating a LDR song? Woah. Her previous work explores the saturated hyper-dreams of consumer capitalism, with presidents dripping in gold chains, Lana herself resplendent in expensive pastel Jackie O suits, or riding across sunset highways against the vintage billboards advertising various American Dreams. The haunting quality of ‘Love’ is that it sort of rises above the glitz and glamour. Smartphones aren’t product placements but rather become anachronistic, incongruous relics, twirling out of time. The youth depicted in ‘Love’ are caught in a static reality, never growing old. By floating into space, they are cast adrift from capitalism’s materialised temporality.
“You get ready you get all dressed up / To go nowhere in particular”. With this line, I’m reminded of an endearing extras video from the Skins series, called ‘Cassie’s dark dates’. Cassie, the ethereal and bittersweet anorexic character, announces to her flatmates that she’s going on a date, slicks on lipstick and smiles nervously in the mirror. She sits in the park smoking in her mustard socks, hair blown back wispy in the wind, watching a red balloon caught in her tree, fragile as her own wee heart. She wanders the city alone till it gets dark, then finds an old man lying on the ground. Thinking he’s dead, she tries to talk to him, then lies down beside him after he says he’s ‘listening to the pavement’. The pair wander home and she helps him make beans and toast; they share a cigarette and some laughter. It’s a lovely depiction of two lost souls from different generations finding temporary peace in their lives. He falls asleep on her knees while she reads an old book. It’s wistfully delightful; watching it now reminds me that those teenagers we watched grow up grotesque and vivid onscreen are somewhere, someone else now. The girl I was ten years ago (literally, wow) is equally lost. Part of her thought she would return to Mars. But she didn’t (or did she?) and instead she faded through the years, through the ether.

Reality is a Stage Set/Baby the World’s Ending
J. G. Ballard famously said that ‘one of the things I took from my wartime experiences was that reality was a stage set’, whereby ‘the comfortable day-to-day life […] could be dismantled overnight’. I’m reminded of the closing scenes of Ashes to Ashes, where Daniel Mays’ devil-like character starts smashing up the office ‘stage set’ and revealing that this reality is really just a kind of limbo, suspended in starry space—all the characters, we suddenly realise, are already dead. This is a series that, as with Life on Mars, is constructed on the premise of a sort of techno-hauntology, where the characters find themselves cast back in time but connected to the present through various forms of twentieth-century media. Signals start crackling with uncanny resonance, spirits and voices carried across the ether.
In ‘Love’, the film’s stage set is revealed as suspended somehow in the rather grandiose setting of space. Seeing the truck spinning, I couldn’t help but be reminded of Gene Hunt’s Quattro, this retro object that acquires nostalgic significance for the contemporary viewer. Why is it hurtling, in Lana’s video, towards the smouldering sun? The faces of the young folk in the car are seen glowing amber as the sun approaches, but they look happy rather than frightened. Somehow the video ends with the cool kids frolicking in this strange environment which could be anywhere, any planet. There are several moons in the sky. There’s a diner in the middle of nowhere. It feels a bit like Mars, all red canyons and desert sands. But there’s the blue water. These sublime landscapes evoke a sense of both fear and wonder as all the characters, including Lana, stare up at the sky. Are they scared of what lies beyond? For a generation whose futures are likely to be less well-off than their parents, whose hopes and dreams are clouded with rent-markets, dead-end jobs, cycles of unemployment and crippling student debt, the world of phantasmagoria evoked by the planets and stars seems a welcome retreat.
Like Clay in Bret Easton Ellis’ Less than Zero, they spend endless time just floating. While Clay drives about on the LA freeways, these characters drive about in their trucks, then frolic in the wastelands of space. What Gen X and millennials have in common is that sense of suspension and boredom. Where millennials differ, perhaps, is in their urge towards something greater, a less jaded sense of existence. When pushed to the edge, where else to go but down into that abyss? Simon Reynolds explains this sense of suspended progress in the twenty-first century, where the problems Ellis’ characters faced in the eighties are even more accelerated within culture and social life:
our belief in progress itself has been shaken badly recently – by the resurgence of faith-based fundamentalisms, by global warming and toxic catastrophe in the Gulf of Mexico, by evidence that social and racial divisions are deteriorating rather than improving, by the financial crisis. In a destabilised world, ideas of durable tradition and folk memory start to appeal as a counterweight and a drag in the face of capitalism’s reckless and wrecking radicalism
(Reynolds 2011: 404).
It’s this drag that Lana’s languid beat creates. She assures us: “It doesn’t matter if I’m not enough / For the future or the things to come”. This is a bold statement in the goal-orientated universe we live in; a time when everything has to be justified, ticked in boxes, underlined with attaching transferable skills. ‘Love’ allows us to dwell on just being, on the non-instrumental connections we make with other humans. Like many LDR videos, ‘Love’ offers a form of escapism from reality, but unlike those other videos this is an escape we all live everyday. The anonymous teenagers/young adults featured in the video could be any of us; they are scaled down, their insignificance is made vivid by the appearance of huge celestial bodies. We literally transcend the Earth. So why not make it spiritual? After all, our planet is itself on the edge. We are living in the time of the Anthropocene. Isn’t it about time our pop-cultural heroine consulted the oracle and told us how best to look westwards?
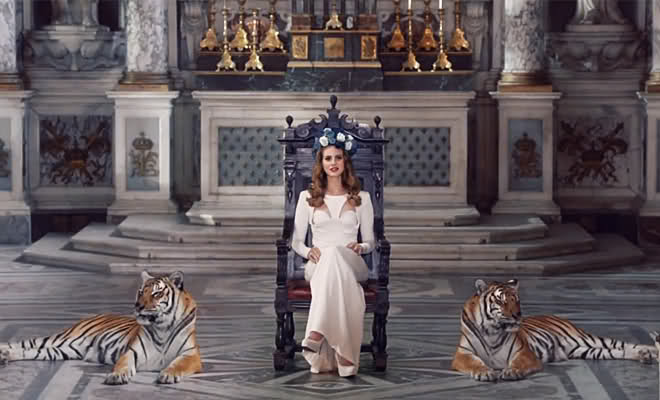


“Baby don’t worry”: Lost in the Chora
Take previous LDR videos. ‘Born to Die’: the American flag, the imperial palace, the denim shorts and red baseball sneakers, tattoos and stretched ears, tigers and headlights, a lost highway, vampy red nails, the virginal white dress, sex, silence, a crown of summer flowers. A glut of signifiers. Money, power, glory. Oh wait, that’s another Lana song. The point is, we’re used to this sort of postmodern meta-play of signifiers when we’re watching a Lana video or listening to a Lana song. Like Ariel Pink, she works with readymade styles, retro-fitted fashions, vintage imagery and iconography. While Pink tends to work with a lo-fi, rough-edged, VHS aesthetic, the juicily plastic styles of the eighties, Lana favours the melancholy Hollywood dreams of the sixties. Those dark lashes, irresistible grin, hair so perfect you could frame it. ‘Love’ is a cinematic video; its very cover art suggests an old-school Hollywood film more than a new single. It’s got grandeur, it rises to what might be called ‘an intergalactic space opera’, although that sounds more like something Muse would get up to. We’re watching shooting stars stream silvery blue over a pyramid. What is a shooting star? A wish? And aren’t wishes necessarily orientated towards the future?
In opposition to an easy play of signifiers, ‘Love’ favours the expansive space of the sensuous and strange. Space itself, understood as whatever that mass of stars and matter that exists beyond our planet, is a bit like Plato’s chora. Or at least, the way it functions in Lana’s video (hell, I’m no astrophysicist). The chora is a kind of ‘mobile receptacle of mixing, of contradiction and movement’ (Kristeva 1977: 57); it is a womblike space which drive flows of renewal and infinite multiplicity within and beyond the subject. Think of a space in perpetual motion, no stasis allowed in its play of atoms. There is always a shimmering, a flickering between being, self, other. The language we use to describe this deconstructive flickering is, as Timothy Morton reminds us, ‘highly accurate’ at ‘a quantum scale’ (2015: 71). ‘When a verb is intransitive,’ he continues, ‘like flicker is, does the fact that it has no direct object mean that it represents a state of being or does it mean that it represents a state of doing—and if so, doing what to what?’ (Morton 2015: 72-73). What if ‘love’, as it appears in Lana’s new single, is an intransitive verb. To be in love is different from saying, ‘I love you’, ‘I love chocolate’ or ‘I love sunsets on the hottest days of June’. You’re not attaching the state to an object. There’s a sense of transition, passage, deferral between expression and feeling, the manifestation of a signifier. The space we inhabit in Lana’s song is a kind of chora, always undergoing some kind of self-rupture.
‘The chora, as rupture and articulations (rhythm), precedes evidence, verisimilitude, spatiality, and temporality’ (Kristeva 2001: 2170). Phantasmagoria are necessarily virtual images, superimposed on reality; the flicker of a hologram, a light display, a shower of fireworks, a neon sign flashing in the darkness. The blur of street-lamps in rain, the light of your phone glowing through a pink gauze of candy-floss, shimmers of fairy lights in a stranger’s window. There’s a sense of being seduced by the other side, by the beyond of the looking glass; nearly getting through but not quite. The allure of the surface, its invitation of depth that mistakes perception for layers of mirrors. The cameras filming ‘Love’ rupture time and space as they burst between different scenes, different worlds. Staring up at the stars is an old-fashioned Romantic image, but it seems less like the humans are projecting themselves onto the landscape, declaring their love as Keats did to the stars: ‘Bright star, would I were steadfast as thou art—’. Rather, this is more an experience of the sublime: the camera’s focus is more on the characters’ eyes, which become reflective screens to the visual dramas unfolding. The world impresses itself upon us, we become but reflective surfaces in the endless refraction of this mysterious universe, its scintillations of colour and light, of divided time.
We view the subject in language as decentering the transcendental ego, cutting through it, and opening it up to a dialectic in which its syntactic and categorical understanding is merely the liminary moment of the process, which is itself always acted upon by the relation to the other dominated by the death drive and its productive reiteration of the “signifier”
(Kristeva 2001: 2175).
With the word ‘liminary’, I can’t help but think of luminary. Is light necessarily a transitive state between presence and darkness? Can one have presence in darkness? A luminary is someone who shines light, who inspires or influences others; but of course it is also a light-giving body, the sun and moon and stars. Lana, clad in white and seeming to emanate light from the stage, is easily the video’s luminary. I also can’t help but think of Walter Benjamin’s Angel of History, ‘turning away from the future to face the ruined landscape of the past’ (Love 2007: 5); she’s caught between past and future, deliberately shadowing the future with her turn to a retro-fitted past.
Liminary, on the other hand, is that which is placed at the beginning of the book; it is the instating moment of ‘the process’. ‘Love’ is the start of something new, even as it is grounded in retro culture. The mise-en-abyme of its central ballroom performance instates a rupture in discourse, the sensuous invitation to revel in its temporal infinitude, the possibility of abyss offered by sudden expansions of space-time, the spreading out into the galaxy. How do we relate to one another in this reconfigured universe, this endless opening of the book that leaves us stranded in the interval between what exists and future artistic possibility? The faces we encounter in the video are always Other, always slipping from our grasp as the camera gives us insufficient time to retain them. What is the signifier so constantly reiterated in ‘Love’? Why, love of course! And here, love is inseparable from death.

No Future: Rejecting Reproductive Futurity
The video’s inertia and the song’s refusal of the little death of musical climax enacts a kind of non-consumerist pleasure. Take a standard pop, rock or indie song. There’s the buildup, the verse/chorus repetitions, the climax (with its attendantly indulgent, masturbatory solo) and the middle eight, a swift denouement. It’s all over before you know it and there you are, gorged and glutted but ultimately empty as you were to begin with. It’s the standard model for masculine sexual desire, which is pretty much always ego-centred. You keep going back for more but the high lasts only as long as the song. ‘Love’ strains towards something more intangible, elastic; both evanescent and eternal, a sensuousness moving between bodies, minds, times—never entirely confined.
I think a clue to the video’s strange temporal dynamics is, perhaps, its conspicuous lack of non-heterosexual couples. If it’s a paean to love, it’s a very straight one. Why have her characters plunge into the fiery planet? Is this a heteronormative apocalypse?

There is a sense that this video is ghosted by a queer temporality. This opens up questions about identity, sexuality but also a more epochal sense of where we are now in terms of our experience of being and time.
According to Walter Benjamin (1940), one of the hallmarks of the modern era is a constant movement through “homogenous, empty time,” as opposed to the hauntings and co-occurrences of premodern civilisations and religious times. Attention to queer temporality explodes the idea of such homogenous and empty time, indicating the public face of white, heterosexual Western normativity as its vanguard.
(Cho 2015: 49)
Another striking thing about ‘Love’ is its white-washing. There are a few mixed-race characters but overwhelmingly these kids are the white youth. Maybe not quite Made in Chelsea-level, but nevertheless the video is pretty white. Now, while there’s been some controversy about Lana’s performative stylisation of racial tropes (and that’s a whole other essay on the topic of cultural appropriation), I don’t think white-washing is an inherent problem with Lana herself; she’s worked with people of colour in previous videos and in her touring band. So this instance of whiteness seems potentially deliberate. It’s part of a more general invoking of this hegemonic bloc, the young folk who we expect to have a wild youth and then grow up and settle into settled, middle-class heteronormative, reproductive lives. But what happens instead? They end up in this performative limbo, this space of the sublime, which is by definition ‘limitless’: ‘the mind in the presence of the sublime, attempting to imagine what it cannot, has pain in the failure but pleasure in contemplating the immensity of the attempt’ (Kant, A Critique of Pure Reason). Lana offers us this impulse to strain beyond what the world, in all its narrow clarity, offers. She urges us to relish in the shadows, even as she emanates light and knowledge.
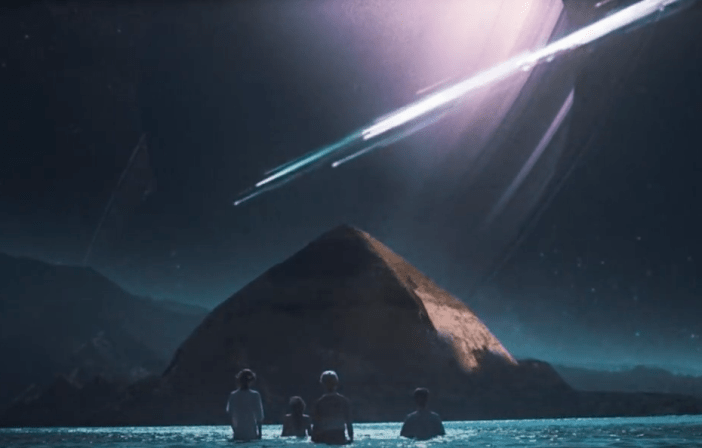
What are these shadows? Where are the queer and non-white hiding? As Lee Edelman (1998) points out, culture and society translate desire into temporality, into narrative; specifically, into the heteronormative teleological narrative of reproductive futurity. Fall in love so you can settle for a single partner, bind your desire in a capitalist social contract based on ideas of possession and commitment (marriage) and then help perpetuate the social order by having children and raising them to share your heteronormative ideologies. ‘Love’ unravels this teleological narrative of love. Those who fall out of the heterosexual camp are considered negative, ghostly, associated with the death drive since they do not reproduce. Lana, with her asynchronous depiction of sixties youth in the age of the smartphone, invokes a kind of time out of joint. As I’ve already said, these kids are trapped in stasis. The chora allows a sensuous, non-object related pleasure that goes beyond the consumer ethic or the typical romantic ethic of attachment. As they enter the waters of Mars (let’s just assume it’s Mars), they spread out from their initial couplings and form a collective of shared wonder. We’ve seen them plunge towards the fiery planet, the possible apocalypse that explodes instead into celestial beauty.
For Edelman, the project of queer theory is to embrace this association with the death drive:
Queer theory, then, should be viewed as a site at which a culturally repudiated irony, phobically displaced by the dominant culture onto the figure of the queer, is uncannily returned by those who propose to embrace such a figural identity within the figuralisation of identity itself.
(Edelman 1998: 27)
As discursive space, queer theory allows for ironically retaliating with an embrace of this phobic backwards queer. So imagery associating homosexuality with ghosts, vampires, absent figures and so on is vividly figured as an assertion of refusal, refusal to capitulate to reproductive futurity. In ‘Love’, the time of adolescence is transformed as these early models for future capitalism become ghosts, faces lit up in celestial white as they form a sort of playful colony on another planet. Their anonymous identities are held in stasis, prompting the audience to conjure for ourselves a narrative for their existence, their future.
By its very exclusion, the queer figure haunts Lana’s video. She reminds us that in Hollywood culture, rarely does a queer character get to share screen pleasure; but ultimately, the couples that do get together in ‘Love’ aren’t doing the old R’nB style dry hump in the back of a fancy car, but rather more innocently share in each other’s being. The moment of collectivity towards the video’s end when everyone looks up at the sky, just as before they looked at Lana, Angel of History, initiates a different kind of shared love. Friendship, perhaps, is just as important as romance. It’s all about a shared openness to the wonders around us. Maybe this is a sort of jouissance, that joy and bliss that cannot be pinned down simply to signifying object relations, ‘the sense of a violent passage beyond the circumscriptions inherent in meaning’ (Edelman 1998: 27). An experience of rupturing pleasure that can poke a hole in our normative sense of reality. However, as with most of Lana’s output, jouissance is inherently tied to the death drive, since by unravelling our symbolic reality, it also peels apart ‘the solidity of every object’, including the subject—making us painfully aware of our finitude, the void that stares back at us through the torn gauze of everyday signification (Edelman 1998: 27).

The Loop of Depression
Often referred to as ‘Hollywood sadcore’, Lana’s music is always inflected with a tragic undertone, a flirting with death (notoriously, she claimed in a Guardian interview that, ‘I wish I was dead already’), an atmosphere of darkness and depression. Depression works often by a loop logic. As Timothy Morton points out, the problem with depression is that it restricts temporality ‘to a diameter of ten minutes’: five in the past and five in the future. This narrowing translates into a kind of loop where one’s inability to think long-term forgoes the possibility of interrupting and re-directing the cycle of negative thought. The beats on ‘Love’ are tensely held; the song rarely develops beyond its repetitive ah-ah-ahs and it’s refrain of young and in love; while on the surface it seems affirmative, really it operates by a loop logic which betrays its cultural claustrophobia, its haunting. As my friend Scott points out, ‘Love’ also has a sound effect ‘that sounds like a metal bolt being locked’ which ‘reinforces how trapped we are in this loop’. And what exactly is this depressive ontology in which we are caught? How does Lana make it so seductive, even as she deconstructs its sources in heteronormative futurity and the existential despair of our millennial generation?
Depressive ontology is dangerously seductive because, as the zombie twin of a certain philosophical wisdom, it is half true. As the depressive withdraws from the vacant confections of the lifeworld, he unwittingly finds himself in concordance with the human condition so painstakingly diagrammed by a philosopher like Spinoza: he sees himself as a serial consumer of empty simulations, a junky hooked on every kind of deadening high, a meat puppet of the passions.
(Mark Fisher 2013: 61)
Being depressed highlights how much of a serial, looped existence we live on a daily basis, regardless of our mental health. It’s just capitalism. Only, unlike their ‘healthier’ or ‘more adjusted’ comrades, the depressed are unable to pursue this consumption of ‘empty simulations’ with any exuberance, feigned or otherwise. What’s the point in washing our hair when we’ll only have to do it again, when we’re not even sure what this body is or who it belongs to or what the fuck it’s doing in the world. When you don’t give a fuck about looking like that girl in the Loreal advert? Sylvia Plath’s protagonist Esther Greenwood, falling into clinical depression, says:
I hadn’t washed my hair for three weeks, either.
I hadn’t slept for seven nights.
The reason I hadn’t washed my clothes or my hair was because it seemed so silly.
I saw the days of the year stretching ahead like a series of bright, white boxes, and separating one box from another was sleep, like a black shade. Only for me, the long perspective of shades that set off one box from the next had suddenly snapped up, and I could see day after day after day glaring ahead of me like a white, broad, infinitely desolate avenue.
It seemed silly to wash one day when I would only have to wash again the next.
It made me tired just to think of it.
I wanted to do everything once and for all and be through with it.
(Plath, The Bell Jar)
The way Plath’s sentences spill out like lines of a poem, of code or fragmentary diary entries, indicate this sense of a loop: Esther can’t think beyond the next five minutes, and when she tries, she sees the infinitude of a ‘desolate avenue’. This is the future of the depressive, an endless repetition of mundanity that has no release from its shade. Esther has lost a sense of purpose or instrumentality: she cannot buy into the ideologies of femininity or self-care that justify the washing of one’s hair. She is, in body and mind, utterly exhausted.
What’s the point in having any faith in television, love, novels—the everyday detritus, landscapes and people of life itself—when everything reveals its inner hollowness, its lack of presence. The depressed see the emptiness in everything, the way everything concatenates, leads back round to the false positive of consumer logic. Maybe it’s a bit like seeing the world through Derrida’s eyes, but without Derrida’s flourishing ability to express it. Being depressed is actually—aside from the myriad debilitating physical and serious mental side effects—about having a very incisive and mostly, sadly, accurate view of the world. The problem is that there are ways of thinking through this loop and creating an alternative, positive subjectivity from the surrounding ruins; but when you’re stuck five minutes into the future and five into the past, this is pretty difficult to achieve.
So in a sense, ‘Love’ fetishises not death per se, but a depressive ontology which overshadows its surface celebration of exuberant love and celestial futurity, the astrological symbolism of possibilities to-come—future predictions. As with Esther Greenwood’s white boxes and black shade, Lana works with a monochrome logic of feedback loops (the audience viewing the artwork which we as audience are presently viewing), the symbiotic, repeated exchange between black and white, presence and absence, past and future. We are gifted with her “vintage music”, with the siren song of the past spreading into the celestial bounds of tomorrow. The sixties were a decade of utopian promise, representing the hope of future freedoms being realised in the present through protest, communes, youth culture—putting new ways of living into practice. In ‘Love’, the stylised invocation of the sixties represents the lost futures which our generation has been outcast from by the structural logic of late capitalism, its favouring of those who came before us, its refusal to invest in the infrastructure of youth and its possibility. The sixties can only appear here in the cinematic vintage of nostalgia.
The sound that comes “through satellites while cruising” could refer to the satellites of the present, the ones that structure the global interconnectedness of the internet, of broadcast television, the possibility of a rhizomatic exchange of divergent (and, hopefully, ideologically and temporally subversive) dreams that goes beyond the one-way projection of Hollywood’s cinematic vision of heteronormative LOVE. The word ‘cruising’ evokes the sense of pointless drifting, the sensuous and pleasurable experience of sailing around without definition of purpose that we find in the chora; in the way the characters float without gravity in space, surrounded by the suspended debris of identity, with smartphones and skateboards. It also, however, connotes the act of wandering around in search of a (casual) sexual partner, a practice often associated with gay culture. Once again, the spectre of the non-heterosexual returns to haunt this vision of sensuous, anti-teleological pleasure. Casual hook-ups rupture the reproductive marriage logic of possession; they instate a consumer attitude of recycled desires. Yet Lana’s video, unlike many contemporary music videos, doesn’t portray a vacuous array of club meet-ups leading to casual sex. It moves towards something sensuous, visionary and strangely warm and beautiful. There’s genuine affect, as Lana smiles and sings her way through this weird journey. She celebrates a kind of jouissance which seems to exist outside of reproductive futurity, outside of capitalism, outside of the Earth as we know it. Is this where we Millennials are headed? Will only the choice, privileged few get to share in this utopia, as is apparent in the video? Whose vintage dream is this, anyway?
Further Reading
Cho, Alexander, 2015. ‘Queer Reverb: Tumblr, Affect, Time’, Networked Affect, ed. by Ken Hillis, Susanna Paasonen and Michael Petit, (London: MIT Press), pp. 43-59.
Fisher, Mark, 2013. Ghosts of My Life: Writings on Depression, Hauntology and Lost Futures (Alresford: Zero Books).
Freud, Sigmund, 1914-1916. ‘Mourning and Melancholia’, On the History of the Psycho-Analytic Movement: Papers on Metapsychology and Other Works, Vol. 14, trans. by James Strachey, (London: Hogarth Press), pp. 243-258.
Heather Love, 2007. Feeling Backward: Loss and the Politics of Queer History (London: Harvard University Press).
Morton, Timothy, 2015. ‘Sparkle Time Time Sparkle’, in Sophie Sleigh-Johnson, Chtonic Index (Southend: Focal Point Gallery), pp. 66-79.
Reynolds, Simon, 2011. Retromania: Pop Culture’s Addiction to Its Own Past (London: Faber and Faber).